1. Molecular characteristics of Boc-Oxyma:
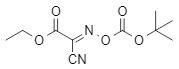
Boc-Oxyma (structural formula shown in Figure 1) combines the amino protection ability of Boc anhydride and the coupling activity of Oxyma, achieving the dual functions of protection reagent and coupling reagent. It has the advantages of high stability, low toxicity, and easy operation, providing a new choice for green chemical synthesis.
Figure 1: Boc-Oxyma structure
2. Dual functional mechanism of Boc-Oxyma:
1. Amino protecting reagent: Breaking through the traditional limitations
The conventional method of introducing tert-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) protecting groups mainly relies on di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc anhydride) and halogenated formate reagents. However, these reagents have several difficulties, including poor stability and purification issues. In contrast, Boc-Oxyma has shown significant technical advantages with its excellent stability, green environmental protection, and wide substrate applicability. Specifically:
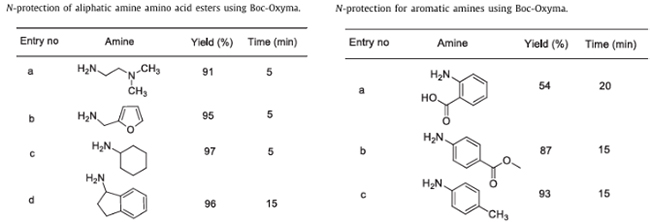
(1) Wide substrate applicability: Effective protection can be achieved for aliphatic amines, aromatic amines, and hindered amines (secondary amines), as shown in Figure 2;
(2) There is an electronic effect regulation: For aromatic amines, following the electronic effect law of aromatic compounds, the presence of electron-donating groups at the ortho-para positions of aromatic amines results in a higher yield (more than 90%), while electron-withdrawing groups will lead to a decrease in reaction yield;
(3) Green reagents: Only a low-toxic byproduct, Oxyma, is generated during the reaction, which can be recycled and reused, effectively reducing waste production and meeting the development requirements of green synthetic chemistry.
Figure 2: Amino group protection experiment involving Boc-Oxyma
2. Coupling reagent: achieving multi-product construction
Boc anhydride is also a coupling reagent, which forms a mixed anhydride intermediate with carboxylic acid and then undergoes a coupling reaction with amino/hydroxyl groups. However, this process easily produces by-products. Boc-Oxyma achieves mild and efficient coupling through the active ester route. Specifically, the technical advantages are as follows:
(1) Construction of multiple functional structures:
① Using carboxylic acid as a substrate:
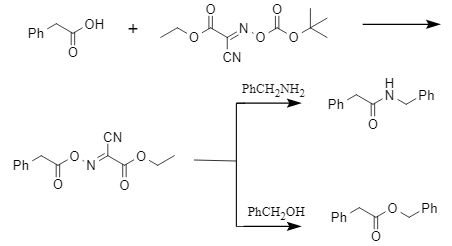
The carboxylic acid coupling reaction promoted by Boc-Oxyma can efficiently construct key functional structures such as ester bonds, thioester bonds, and amide bonds. It exhibits universal activation ability for fatty acids, aromatics, long-chain compounds, and amino acids. Taking the phenylacetic acid model reaction as an example, the coupling efficiency with benzyl alcohol and benzylamine can reach more than 90%. The mechanism of action of Boc-Oxyma is to form an oxyanhydride active ester of carboxylic acid, followed by nucleophilic attack to complete the bonding process, as shown in Figure 3:
Figure 3: Mechanism of action of Boc-Oxyma
② Using hydroxamic acid as substrate:
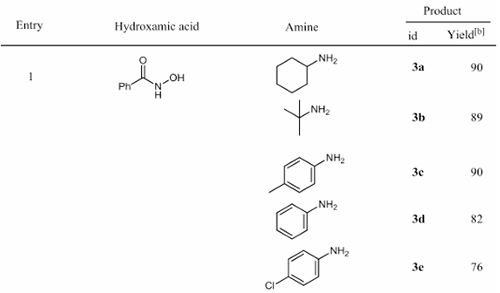
With the participation of Boc-Oxyma, hydroxamic acid undergoes a Lossen rearrangement reaction to obtain the corresponding isocyanate. Under the action of amine nucleophiles, the corresponding urea derivatives can be obtained by room temperature reaction (as shown in Figure 4). Compared with the traditional Hofmann reaction, which requires high-valent iodine and the Curtius reaction involving azide, it is safer and milder.
In addition, in the system where hydroxyl and amino groups coexist, it can selectively react with amino groups at room temperature to generate urea derivatives, while when alcohol/thiol participates in the reaction, DMAP catalysis and heating are required to obtain the corresponding carbamate and thiocarbamate compounds.
Figure 4. Boc-Oxyma-mediated hydroxamic acid coupling reaction
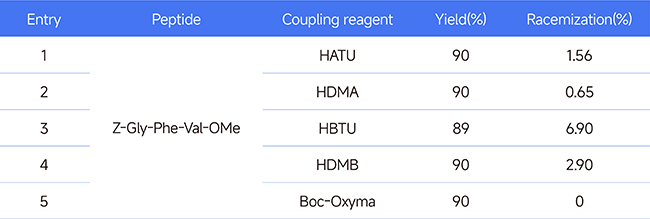
(2) Stereoselective regulation: Taking the synthesis experiment of tripeptide as an example,
Boc-Oxyma not only has an efficient coupling ability but also excels in controlling the stereostructure. In the comparative experiment on the racemization of tripeptide synthesis, Boc-Oxyma performed outstandingly, with no racemization phenomenon detected. See Table 1 below for details:
Table 1 Racemization comparison test
(3) Green and sustainable reaction system
The Boc-Oxyma system has outstanding performance in terms of atomic economy and green environmental protection:
① Most of the coupling reactions in which it participates are carried out at room temperature, with low energy consumption;
② Its by-product, Oxym, can be recycled and reused, with a high utilization rate and low cost;
③ The remaining by-products (tert-butyl alcohol, carbon dioxide) are low-toxic, and the discharge of the three wastes is relatively small.
In summary, Boc-Oxyma significantly improves the economic efficiency of synthesis due to its "one dose for multiple uses" characteristics, provides a new synthetic idea for peptide synthesis and industrial production, and has important application value and potential.
After 22 years of relentless efforts and accumulation, Highfine Bio has continued to deepen its roots in the field of global peptide synthesis reagents. It has now developed into a leading company with extensive customized product coverage capabilities and significant advantages in large-scale production. It can now supply Boc-Oxyma products of various specifications to meet the specific needs of different customers. We sincerely invite customers interested in this product to contact us to learn more about the product details and explore potential cooperation opportunities.
References:
[1] Robert, AR; Kumar, GR; Jonnalagadda, SB, et al.. A novel use of Boc-Oxyma as a reagent for tert-butoxycarbonylation of amines and amino acid esters[J]. Chemical Data Collections, 2020, 30.
[2] Thalluri, K.; Nadimpally, KC; Mandal, B.; et al. Ethyl 2-(tert-Butoxycarbonyloxyimino)-2-cyanoacetate (Boc-Oxyma) as Coupling Reagent for Racemization-Free Esterification, Thioesterification, Amidation and Peptide Synthesis[J]. Adv. Synth. Catal.., 2013, 355, 448–462.
[3] Manne, SR; Thalluri, K.; Mandal, B.; et al. Ethyl2-(tert-Butoxycarbonyloxyimino)-2-cyanoacetate (Boc-Oxyma): An Efficient Reagent for the Racemization Free Synthesis of Ureas, Carbamates and Thiocarbamates via Lossen Rearrangement[J]. Adv. Synth. Catal.., 2017, 359, 168–176.