In response to the aforementioned problems, Yao Zhujun's team at Nanjing University developed an immobilized molecular reactor (RMMRs) based on the acyl transfer mechanism of ribosomes.
RMMR Introduction:
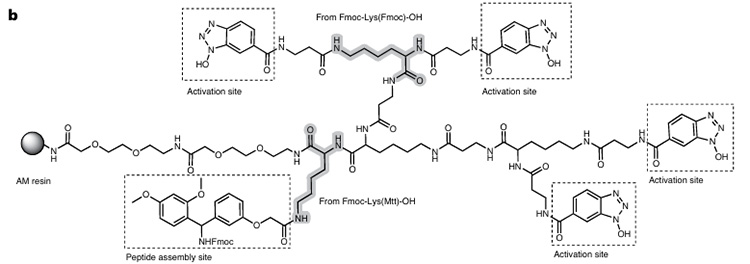
RMMR resin is based on Rink amide resin, with dendritic dispersed activation sites constructed through Fmoc-Lys derivatives, and finally fixed on AM resin (Figure 1). Its swelling capacity is comparable to that of commercial resins, and it has good stability with no degradation within 6 months.
Figure 1. Composition of RMMR
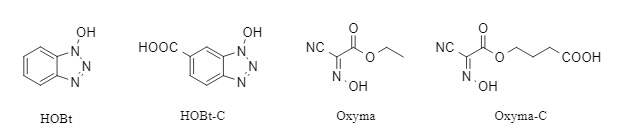
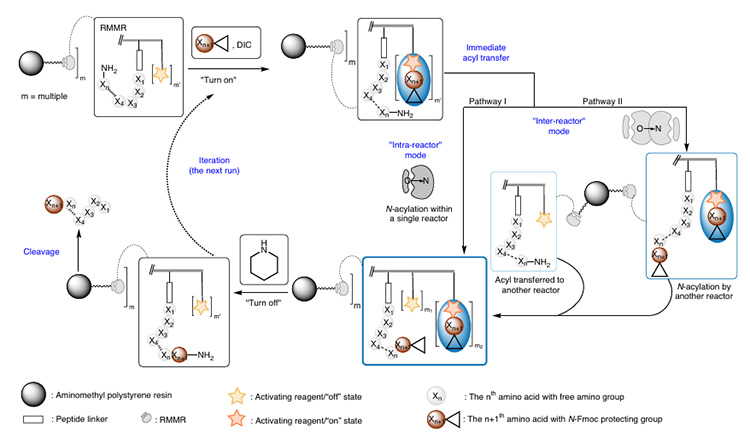
This reactor connects four carboxyl activation sites (see Figure 2) and one peptide synthesis site to the resin. In the presence of DIC and N-Fmoc amino acids, multiple active ester intermediates are formed, promoting rapid intramolecular or intermolecular O→N acyl transfer between the N-terminal amino group and adjacent activation intermediates (only one oxyacyl group is coupled), thereby improving the synthesis efficiency of sterically hindered peptides. Finally, treatment with piperidine simultaneously removes the Fmoc protecting group and regenerates unreacted active esters. Its mechanism of action is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 2. Universal active activators and their derivatives
Figure 3 Mechanism of action of RMMRs
RMMR Applications:
1. Conventional Peptide Synthesis
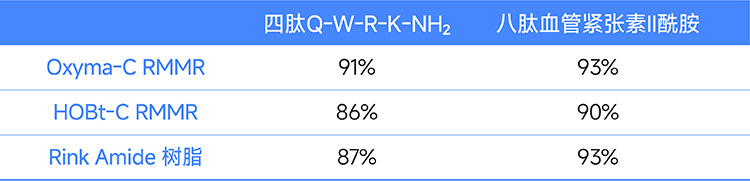
In the conventional peptide synthesis, the tetrapeptide QWRK-NH2 and the octapeptide angiotensin II amide were synthesized using RMMA resin with Oxyma-C and HOBt-C as active sites and commercial Rink Amide resin, respectively. The results are compared in the table below.
Table 1. Comparison of results of tetrapeptides and octapeptides synthesized with different resins
![Comparison of results of tetrapeptides and octapeptides synthesized with different resins Comparison of results of tetrapeptides and octapeptides synthesized with different resins]()
Note: The values in the table represent the purity of the crude product.
Experimental results show that peptides synthesized with RMMR resin are comparable in quality to those synthesized with commercial Rink Amide resin. Furthermore, the purity of the crude product obtained using Oxyma-C RMMR resin in manual synthesis mode is 97%, while the purity of the automated synthesis mode is 94%, showing similar results between the two methods.
2. Steric Hindered Peptide Synthesis
(1) Synthesis of N-Methylated Peptides
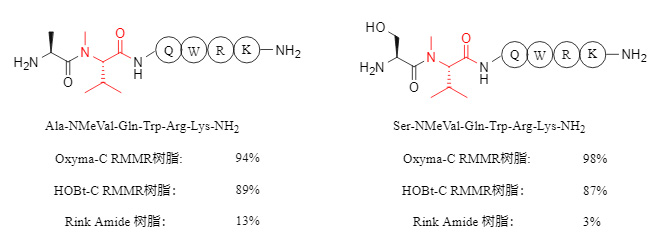
In the synthesis of peptides containing N-methylated amino acids, RMMR resin significantly improves the condensation efficiency, with product purity reaching up to 98%, while the purity of products obtained using Rink Amide resin is mostly below 20%. Some examples are shown in Figure 4 below.
![Synthesis of N-methylated peptides using different resins Synthesis of N-methylated peptides using different resins]()
Figure 4. Synthesis of N-methylated peptides using different resins
(2) Synthesis of α,α-disubstituted peptides:
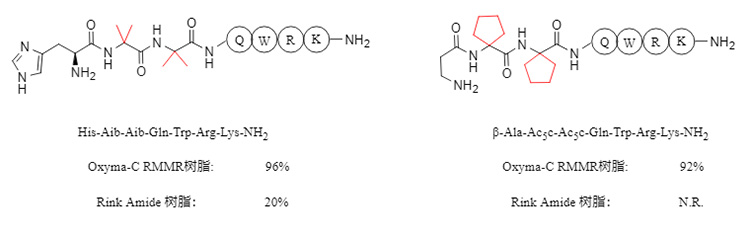
RMMR resin also exhibits excellent synthetic ability when synthesizing peptides containing α,α-disubstituted amino acids (such as Aib, α-aminoisobutyric acid). For sequences containing two consecutive α,α-disubstituted amino acids (as shown in Figure 5 below), the purity can reach over 90%. In contrast, commercially available Rink Amide resin is difficult to synthesize the corresponding peptides effectively.
![Synthesis of continuous α,α-disubstituted peptides using different resins Synthesis of continuous α,α-disubstituted peptides using different resins]()
Figure 5. Synthesis of continuous α,α-disubstituted peptides using different resins
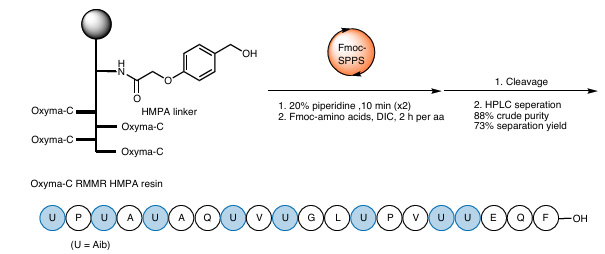
(3) Synthesis of complex molecular alamitecin F analogues
![Synthesis of alamethicin F analogues Synthesis of alamethicin F analogues]()
Figure 6 Synthesis of alamethicin F analogues
To further verify the applicability of RMMR resins in complex structures, the team synthesized an alameticin F analog containing eight Aib residues using Oxyma-C RMMR resin. Experimental results showed that RMMR resins are equally efficient for complex sterically hindered peptides: the purity of the crude product obtained could reach up to 88%, and the separation yield also reached 73%.
These experiments demonstrate that RMMR resins, through their immobilized acyl transfer mechanism, overcome the limitations of traditional solid-phase synthesis in preparing sterically hindered peptides, significantly improving condensation efficiency.
Overall conclusion:
The RMMR series of resins provides an efficient and reliable solution for synthesizing sterically hindered peptides with pharmaceutical potential by mimicking the acyl transfer mechanism of ribosomes, particularly excelling in the introduction of N-methylated and α,α-disubstituted amino acids. Furthermore, the synthesis of challenging amino acids using this series of resins requires only commercially available Fmoc amino acids and DIC reagents, and is compatible with both manual and automated synthesis modes, demonstrating broad application prospects.
Company Introduction:
After 22 years of unremitting efforts and accumulation, Haofan Biotech has continued to cultivate the global peptide synthesis reagent field and has now developed into a leading enterprise with extensive customized product coverage and significant advantages in large-scale production, which can meet the specific needs of various customers. We sincerely invite customers who are interested in this product to contact us to learn more about the product details and explore cooperation opportunities.
References:
[1] Wei, S.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Z., et al. Immobilized acyl-transfer molecular reactors enable the solid-phase synthesis of sterically hindered peptides[J]. Nat. Chem. 2025, 17, 1596−1606.