Table 1 Solubility of DSC in organic solvents
| Solvent |
Dichloromethane |
acetone |
Acetonitrile |
Tetrahydrofuran |
Ethyl acetate |
Isopropyl alcohol |
DMF |
DMSO |
| Solubility (mg/mL) |
2 |
14 |
34 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
88 |
>250 |
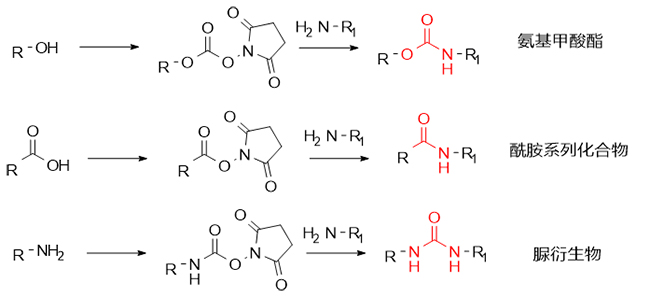
DSC has a wide range of applications in peptide synthesis, drug design, nucleic acid modification and other fields. Its mild reaction conditions and high-efficiency coupling characteristics make it play an important role in the synthesis of urea derivatives and carbamate compounds. At the same time, DSC is also a commonly used coupling reagent for amides and thiophospholipids. By promoting the formation of carbonates, carboxylic acid active esters and corresponding carbamate succinimidyl esters, further reacting with amine molecules, the corresponding carbamate, amide and urea derivatives are efficiently synthesized (as shown in Figure 1).
Figure 1 DSC-mediated synthesis pathway
I. Synthesis of carbamate compounds
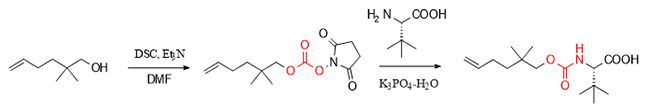
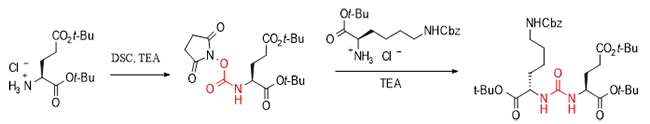
Carbamate compounds have attracted much attention due to their wide range of applications and their importance in medicine, pesticides, coatings, and organic synthesis. DSC, as an efficient activator, can not only promote the synthesis of carbamate compounds from alcohols and hindered amino acids, but also play a core role in the key synthesis steps of carbamate series drugs such as the HIV treatment drug darunavir, and realize the splicing of complex molecular fragments in biochemistry.
Specifically, in the synthesis of the key intermediate of the anti-hepatitis C drug vanirvir, DSC efficiently synthesized the target carbamate compound by activating alcohol and then reacting with L-tert-leucine, which has a large steric hindrance.
In the synthesis of the HIV drug darunavir molecule, DSC achieved the splicing of two key fragments by forming an activated ester with a hydroxyl group.
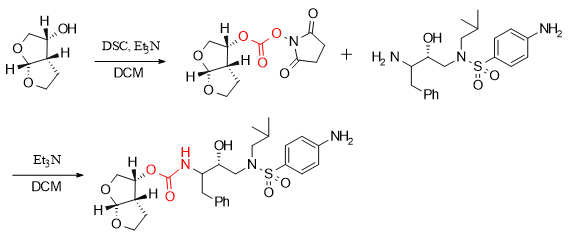
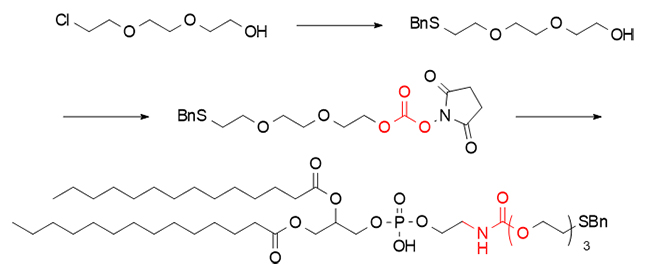
In addition, in the synthesis of thiophospholipids, DSC also demonstrated its excellent coupling performance. By activating with hydroxyl groups and then splicing with the amino group of DMPE, thiophospholipids connected by carbamate bonds were achieved.
2. Synthesis of urea derivatives
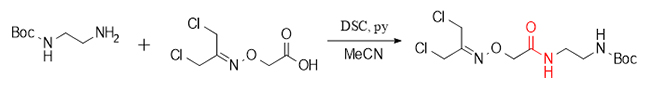
Urea functional fragments, as key structures in many drug molecules, play an important role in regulating molecular activity and physicochemical properties. In the synthesis of the radioactive imaging agent Piflufolastat F-18, DSC generated succinimide ester intermediates by reacting with amino groups, and further constructed urea structural fragments, demonstrating its flexibility and efficiency in drug synthesis.
3. Synthesis of amide series compounds
Amide compounds are the most basic structural fragments in the field of peptide synthesis and are also key structures in the field of drug synthesis. As an activation and protection agent, DSC has demonstrated its versatility in chemical synthesis. It can not only form carbonates and succinimide esters, but also form active esters with carboxyl groups, and further form stable amide compounds with amine groups.
In summary, the wide application of DSC in the fields of chemistry, medicine, and biology demonstrates its important position in organic synthesis. Whether it is promoting the synthesis of complex molecules or its application in basic chemical reactions, DSC has demonstrated its excellent reaction performance and is an indispensable tool in the hands of researchers.