1. Introduction to Compounds
| project |
Disodium p-nitrophenyl phosphate |
| CAS |
333338-18-4 |
| Molecular weight |
371.2 |
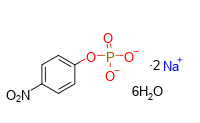
| Structural formula |
![highfine highfine]() |
| Chemical formula |
C6H4NO6P 2Na 6H2O |
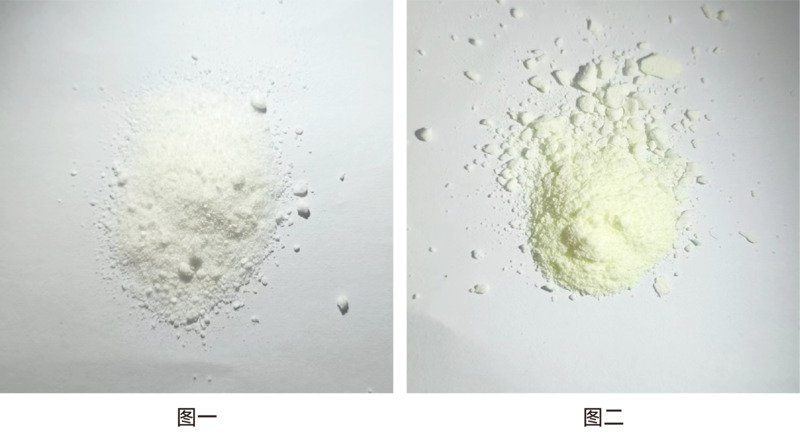
| Exterior |
White to pale yellow solid |
Disodium p-nitrophenyl phosphate, also known as 4-nitrophenyl phosphate disodium salt hexahydrate, abbreviated as PNPP, is an important chemical intermediate in the field of pharmaceutical pesticide synthesis and a phosphorylation reagent in nucleotide synthesis. PNPP is widely used in biomedicine. It was first used in clinical practice to detect alkaline phosphatase activity in serum. With the development of research, PNPP can also be used as a general indicator of phosphohydrolase activity, mainly used as a marker of alkaline phosphatase activity in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and conventional spectrophotometry. The following is an introduction to its principles and applications to better understand its application value in biomedical research.
2. Principle and application
The working principle of PNPP is that colorless disodium p-nitrophenyl phosphate decomposes under the catalysis of alkaline phosphatase, and the generated p-nitrophenol is converted into p-nitrophenol anion under alkaline conditions, resulting in a shift in the long-wave direction, that is, the water-soluble product is yellow, so the purpose of monitoring the reaction process can be achieved by monitoring the absorption around 410 nm.
The application of PNPP in biomedicine is of great significance for disease diagnosis and treatment. Specifically, it can be used to determine the catalytic activity of various phosphatases.
Alkaline phosphatase (abbreviated as ALP), also known as alkaline phosphatase, is one of the commonly used marker enzymes in in vitro diagnostic reagents. It is widely distributed in human tissues such as liver, bones, intestines, kidneys and placenta. It is an enzyme excreted from the liver to the bile. Common ones include intestinal alkaline phosphatase, non-tissue-specific alkaline phosphatase, placental alkaline phosphatase, etc. Under alkaline conditions, it can catalyze the hydrolysis of phosphate bonds, thereby exposing the hydroxyl groups in the substrate molecules. Such substrates include nucleic acids (DNA, RNA), proteins, alkaloids, etc. In biology, changes in the level of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and the level of its activity are often used as an indicator to detect tissue behavior. The detection of alkaline phosphatase can be used to diagnose diseases such as abnormal liver function, osteoporosis and diabetes.
In addition, PNPP is a commonly used ELISA substrate for alkaline phosphatase detection. ELISA is a commonly used immunoassay technique that can be used to detect biological molecules such as proteins, hormones, cytokines, etc. in samples. ELISA detection has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, and simple operation, so it is widely used in biomedical research. PNPP, as a substrate for ELISA detection of alkaline phosphatase, plays an important role in biomedical research.
In summary, PNPP is a very popular in vitro diagnostic reagent. This article briefly introduces the application of PNPP in biomedicine. In addition, PNPP can also be used for pesticide residue detection, etc. It is an important chemical intermediate in the field of medicine and pesticides. Due to the application of PNPP in the biomedical field, its quality has an important impact on medical testing. The following figures are the properties of qualified (one) and unqualified (two) quality. Haofan Bio is currently supplying PNPP, and its quality meets or exceeds industry standards.
In addition, the company is committed to the research and development and production of amide and peptide synthesis reagents. After twenty years of development and accumulation, the company has become the world's largest and most comprehensive supplier of amide synthesis reagents. Friends are welcome to call for inquiries.