Among the many condensation reagents, ionic condensation reagents such as HATU are widely used due to their high reactivity and excellent racemization suppression. However, these reagents contain high-energy heteroatom bonds (such as N-N and N-O bonds), resulting in poor thermal stability and potential safety risks. To address this, Kunishima's team developed a new condensation reagent, 2-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate, abbreviated as DMT-TU.
1. Molecular characteristics of DMT-TU:
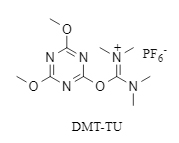
DMT-TU innovatively combines the high reactivity of the tetramethylurea structure and the easy-leaving properties of the triazine structure in DMTMM (see structure in Figure 1). It has both high reactivity and the ability to inhibit racemization. The molecule does not contain high-energy heteroatom bonds, which improves stability. Experiments have shown that it remains stable after being stored in a refrigerator for one year.
Figure 1 DMT-TU structure
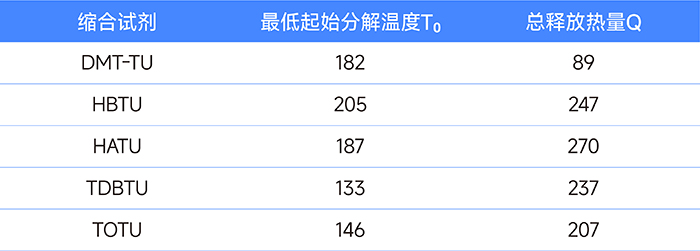
In addition, the thermal properties of DMT-TU and other condensation reagents were evaluated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The data of the lowest onset decomposition temperature T0 and the total released heat Q are as follows:
As can be seen from the table, the decomposition temperature of DMT-TU is comparable to that of HATU, but its total released heat is significantly lower than that of the condensation reagent, indicating that it has higher safety during use and storage.
2. Mechanism of action of DMT-TU:
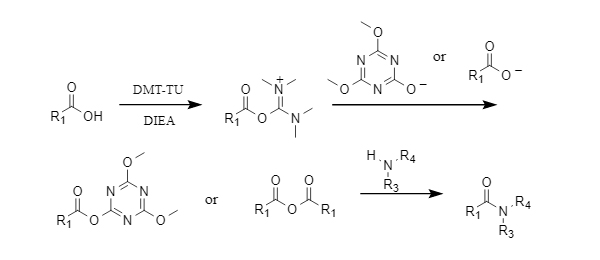
The mechanism of action of DMT-TU is as follows: carboxylic acid reacts with DMT-TU in the presence of a base to form O-acylisourea, which is then further reacted with triazinate or carboxylate to form the corresponding triazine ester or carboxylic anhydride, and finally aminolysis to obtain an amide compound.
Figure 2 Mechanism of action of DMT-TU
3. Functions of DMT-TU:
1. Highly Efficient Coupling Ability:
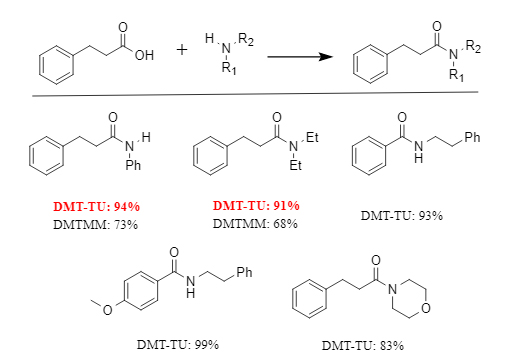
DMT-TU can efficiently construct amide bonds and is suitable for both aromatic and aliphatic substrates, with reaction yields generally exceeding 80% (see figure for details). In the reaction of phenylpropionic acid as a model substrate with aniline/diethylamine, yields exceeding 90% were achieved using DMT-TU. Under the same conditions, the corresponding amide yields using DMTMM were 73% and 68%, respectively. This demonstrates that DMT-TU exhibits superior reactivity.
Figure 3 Condensation reaction promoted by DMT-TU
2. Excellent racemization inhibition performance
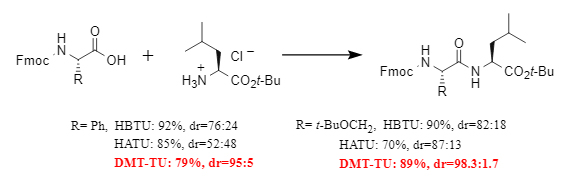
In addition to high reactivity, an excellent condensation reagent must also possess strong racemization inhibition capabilities. In comparative experiments with racemizable amino acid substrates, DMT-TU demonstrated excellent racemization inhibition, achieving a lower racemization ratio than traditional reagents such as HATU and HBTU (see Figure 4).
In summary, the new condensation reagent DMT-TU achieves a combination of high activity and high safety through ingenious molecular design. It is a potential industrial condensation reagent and also provides new ideas for the further development of peptide synthesis technology. It has important scientific research and application value.
After 22 years of unremitting efforts and accumulation, Haofan Bio has continued to deepen its roots in the field of global peptide synthesis reagents and has now developed into a leading company with extensive customized product coverage capabilities and significant large-scale production advantages, which can meet the specific needs of various customers. We sincerely invite customers who are interested in this product to contact us for further information on the product and to explore cooperation opportunities.
References:
[1] Mizushima, G.; Fujita, H.; Kunishima, M. Development of a Triazinyluronium-Based Dehydrative Condensing Reagent with No Heteroatomic Bonds[J]. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 89, 18660−18664.