1. Differences between different grades of chloroform reagents
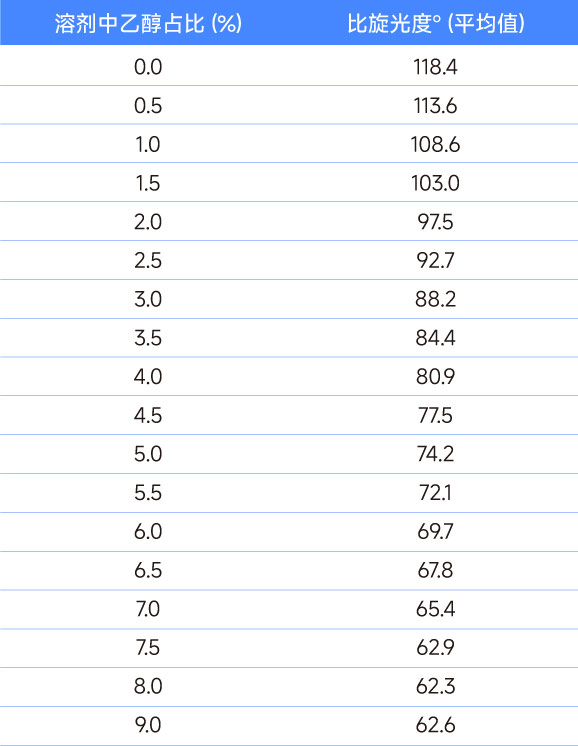
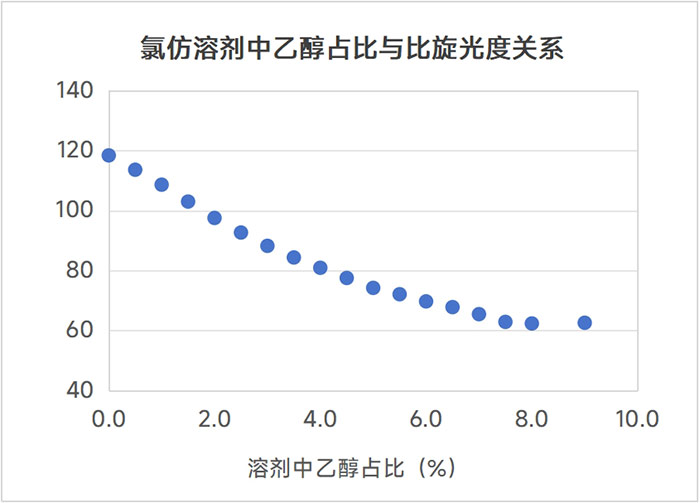
According to the literature, we used chloroform solvent to prepare samples for the specific rotation determination of this compound. Naturally, we used analytical grade (AR) reagents. However, when our data showed a big difference with the customer's data, we used higher-grade chromatography (HPLC) grade reagents to re-prepare the sample and found that the specific rotation of the compound was much larger than the original data. Considering that chloroform may be oxidized by light to produce hydrogen chloride (HCl), which in turn affects the compound, we measured the pH value of the chloroform reagent and found no problem. Finally, we checked the COA of chloroform and found that AR-grade chloroform reagents contain a certain amount of ethanol (domestic standard 0.3%-1%) to ensure the stability of chloroform, while the ethanol content in domestic HPLC-grade chloroform reagents is not indicated, so we think it is 0%. The general idea is that such a small amount of ethanol content will not have a big impact on the determination of specific rotation. However, our experimental results show that the specific rotation of the same compound in AR solvent and HPLC solvent has an error of more than 6%. To this end, we added different amounts of ethanol to the AR-grade chloroform reagent and then performed a series of specific rotation tests on the compound. We found that the ethanol content in chloroform had a great influence on the specific rotation of the compound, as shown in Figure 1.
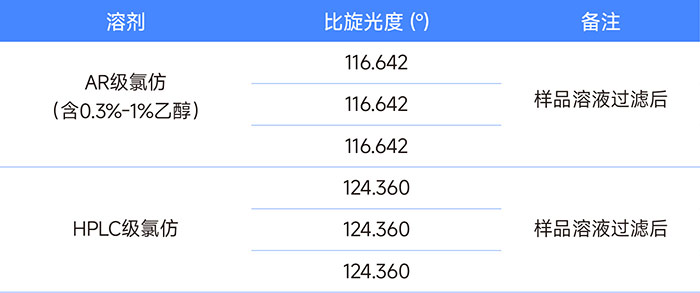
The same compound obtained specific rotations of 116.64 and 124.36 in AR solvent and HPLC solvent, respectively. This shows that in HPLC-grade chloroform reagent, the ethanol content is basically determined to be or close to 0%, and the AR-grade reagent we use contains about 0.75% ethanol. Different companies may use specific levels of reagents to configure test samples according to their own standard operating procedures. This must be clarified and verified when communicating between companies.
Table 1: Relationship between specific optical rotation and the proportion of ethanol in the solvent
(Does not include the ethanol content in AR-grade reagent chloroform)
Figure 1: Relationship between specific optical rotation and the proportion of ethanol in the solvent
(Does not include the ethanol content in AR-grade reagent chloroform)
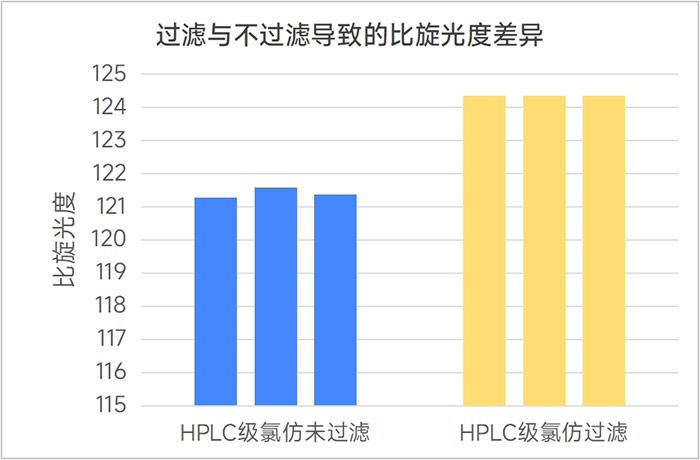
2. The difference between filtering and not filtering
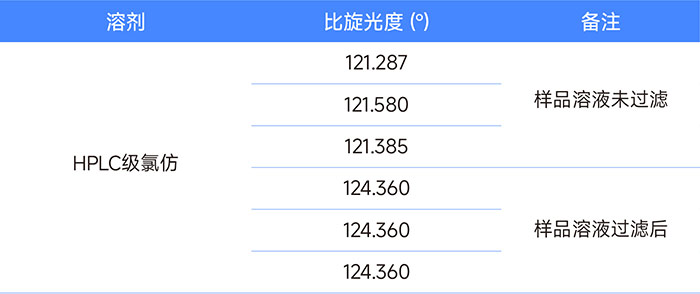
During this investigation, we also found that the floating small particles in the solution that are invisible to the naked eye have a great impact on the stability of the optical rotation test. After filtering the sample solution with a 0.22 μm organic filter membrane, the sample test results are completely consistent within the (3 decimal places) significant figures of the test data given by the instrument, showing extremely high repeatability.
Table 2 Differences in specific rotation results between HPLC-grade and AR-grade chloroform solvents
Table 3 Differences in specific rotation results caused by filtering and not filtering sample solutions (same solvent)
Figure 3: Difference in specific rotation caused by filtering and not filtering the sample solution (same solvent)
Conclusion
The occurrence and investigation of this problem made us realize more deeply that in formulating test conditions, we must not only use high-standard reagents and chemicals, but also have a detailed and sufficient understanding of the materials and items used, including reagents, and indicate them in the operating procedures to ensure that the best test results with high repeatability and accuracy are obtained under reasonable test conditions.
Note: The polarimeter used in this article is: AUTOPOL I, an automatic polarimeter from Rudolph Research Analytical, USA, with a temperature control of 20°C.